BCI-DNI Atlas
A high-resolution anatomical MRI atlas with structural parcellation of the brain
Developed by Anand A. Joshi, Soyoung Choi, Jessica L. Wisnowski, Justin P. Haldar, David W. Shattuck, Hanna Damasio, and Richard M. Leahy
The BCI-DNI Brain Atlas is included with the BrainSuite distribution, which can be downloaded here. When using the BCI-DNI Brain Atlas in your published work, please cite the following reference paper:
Atlas Description
The BCI-DNI Brain Atlas was prepared using a high-resolution (0.5 mm × 0.5 mm × 0.8 mm) 3D MPRAGE scan of a right-handed adult woman in her mid-thirties, acquired at USC’s Dornsife Cognitive Neuroscience Imaging Center on a 3T Siemens MAGNETOM Tim Trio scanner. It is a brachicephalic brain.
The MPRAGE image was processed in a semi-automatic fashion using BrainSuite with meticulous manual corrections of the skull-stripping, cerebrum, and white-matter masks using the BrainSuite GUI interface and included a semi-automated bias field correction using the BFC Correction tool (http://neuroimage.usc.edu/neuro/Resources/bfc_correction_tool). All volumetric labels and sulci were drawn manually by Hanna Damasio, author of the human brain atlas, “Human Brain Anatomy in Computerized Images” (Oxford University Press, 2005) and Director of the Dornsife Cognitive Neuroscience Imaging Center (DNI) at the University of Southern California. The Sulcal Tracing Protocol [1] can be found here http://neuroimage.usc.edu/CurveProtocol.html.
The transfer of the volume labels to the surface mesh was done automatically using SVReg processes and hand-perfected using a Sulci-Surface Correction tool.
All extractions and manual corrections were performed by Soyoung Choi and approved by Hanna Damasio.
Image Acquisition
0.5 mm x 0.5 mm x 0.8 mm MPRAGE image. 384 x 384 x 192 matrix size with a 210 mm x 210 mm x 154 mm FOV.
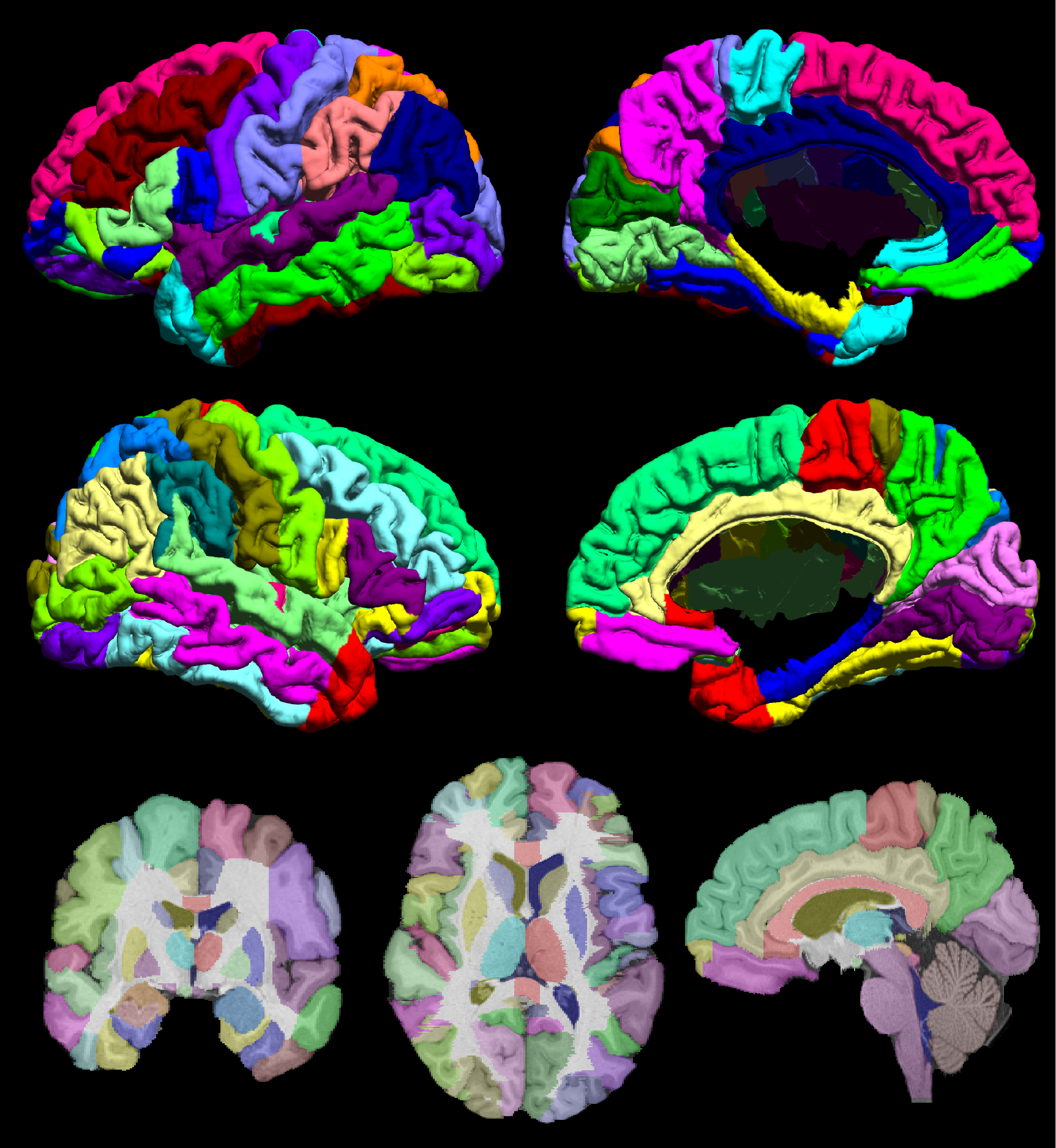
Fig. 1. The BCI_DNI Brain Atlas The figure shows the mid-cortical surface of the BCI-DNI brain atlas, color coded for each parcellated region. Labeled left (top row) and right (bottom row) hemisphere and mesial (right column) and lateral (left column) mid-cortical surfaces. (bottom row) Single-slice skull-stripped MPRAGE image with labels overlaid on coronal (left), axial (middle) and sagittal (right) orientation.
Usage
Detailed instructions for using the BCI-DNI brain atlas with BrainSuite, FreeSurfer, and FSL are available here.
Regions of Interest
95 ROIs are delineated on the volumetric labels of the atlas. 66 of these regions are labeled on the surface.
superor frontal gyrus
middle frontal gyrus
pars opercularis
pars triangularis
pars orbitalis
pre-central gyrus
transvers frontal gyrus
gyrus rectus
middle orbito-frontal gyrus
anterior orbito-frontal gyrus
posterior orbito-frontal gyrus
lateral orbital gyrus
paracentral lobule
cingulate gyrus
subcallosal gyrus
post-central gyrus
supramarginal gyrus
angular gyrus
superior parietal gyrus
pre-cuneus
temporal pole
superior temporal gyrus
transverse temporal gyrus
middle temporal gyrus
inferior temporal gyrus
fusiforme gyrus
parahippocampal gyrus
hippocampus
amygdala
superior occipital gyrus
middle occipital gyrus
inferior occipital gyrus
lingual gyrus
cuneus
Insula
caudate nucleus
putamen
globus pallidus
nucleus accumbens
thalamus
inferior colliculus
superior colliculus
mamillary body
pineal
lateral ventricles
third ventricle
fourth ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
brainstem
corpus callosum
cerebellum
Sulci
26 sulci on each hemisphere are marked according to the BrainSuite curve protocol [1]. Details can be found at http://neuroimage.usc.edu/CurveProtocol.html
Additional sulci are marked on a second set of curves totaling 39 sulci on the left hemisphere and 37 sulci on the right hemisphere.
*indicates sulci described in the original BrainSuite curve protocol.
central sulcus*
precentral sulcus*
superior frontal sulcus*
inferior frontal sulcus*
ascending branch of the sylvian fissure*
horizontal branch of the sylvian fissure*
diagonal sulcus
lateral orbital sulcus*
frontomarginal sulcus*
cingulate sulcus*
paracentral sulcus*
superior supra orbital sulcus*
inferior supra orbital sulcus
olfactory or medial orbital sulcus*
H shaped sulci, mesial
H shaped sulci, lateral
H shaped sulci, transverse
sylvian fissure terminal split *
superior temporal sulcus*
inferior temporal sulcus*
occipito temporal sulcus*
collateral or medial occipito temporal sulcus*
transverse temporal sulcus*
circular sulcus*
postcentral sulcus*
intraparietal sulcus*
primary sulcus of Jensen
secondary sulcus of Jensen
parieto occipital sulcus*
subparietal sulcus*
calcarine sulcus*
calcarine sulcus terminal T
transverse occipital sulcus*
superior lateral occipital sulcus
inferior lateral occipital sulcus
anterior occipital sulcus
References
[1] Pantazis D, Joshi AA, Jintao J, Shattuck DW, Bernstein LE, Damasio H, and Leahy RM, Comparison of landmark-based and automatic methods for cortical surface registration, NeuroImage, Vol. 49(3), pp 2479-2493, 2009.