BDP: Flags
BDP provides numerous optional flags to change the default behavior of different steps of the pipeline. Following are general usage options:
Usage:
bdp.sh <BFC FILE> [OPTIONAL FLAGS] --nii <NIFTI FILE> --bvec <GRADIENT FILE> --bval <B-VALUE>
bdp.sh <BFC FILE> [OPTIONAL FLAGS] --nii <NIFTI FILE> --bmat <BMAT FILE>
bdp.sh --no-structural-registration [OPTIONAL FLAGS] --output-fileprefix <fileprefix>
bdp.sh --no-structural-registration [OPTIONAL FLAGS] --nii <NIFTI FILE> --bvec <GRADIENT FILE>
--bval <B-VALUE>
bdp.sh --no-structural-registration [OPTIONAL FLAGS] --nii <NIFTI FILE> --bmat <BMAT FILE>
bdp.sh --check-for-updates
bdp.sh --version
bdp.sh --help
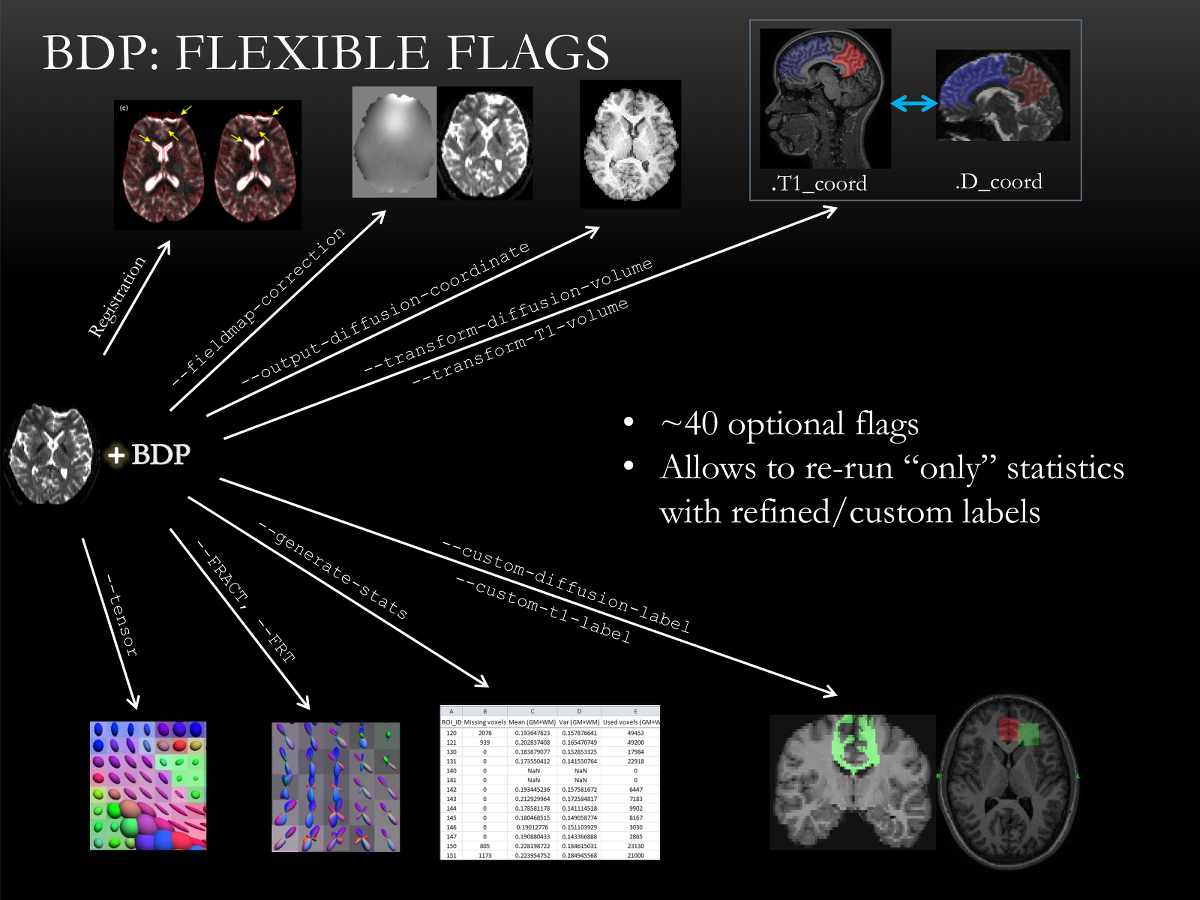
Here is a short (and incomplete) list of different functionality provided by optional flags. Please go through the exhaustive list of all flags in next section.
- Display details of all flags and version information via
--help - Check for new BDP releases via
--check-for-updates - Save outputs to in native diffusion coordinates, in addition to T1-coordinates, via
--output-diffusion-coordinate. This applies to almost all possible outputs including diffusion tensors, ODFs and statistics. - Specify output sub-directory via
--output-subdir. It will save all output files in the specified sub-directory. This can help to avoid file cluttering. - Specify custom masks for structural and diffusion images via
--t1-maskand--dwi-mask - Specify direction of EPI distortion via
--dir=<direction> - Select distortion correction mode (more details):
- Registration-based distortion correction (default)
- Fieldmap-based distortion correction via
--fieldmap-correction - No distortion correction via
--no-distortion-correction
- Specify type of diffusion parameters to be estimated:
- Diffusion tensor (default)
- ODFs using FRACT via
--FRACT - ODFs using ERFO via
--ERFO - ODFs using 3D-SHORE via
--3DSHORE - ODFs using FRT via
--FRT - ODFs using GQI via
--GQI - Change regularization parameter of the Laplace-Beltrami operator while estimating ODFs via
--odf-lambda
- Compute ROI-wise statistics via
--generate-stats. More options:- Re-run only statistics (and skip all registration and tensor estimation steps) with manually refined ROIs via
--only-generate-stats - Run statistics on custom ROIs and masks via
--custom-diffusion-labeland--custom-t1-label - Compute statistics only on selected ROIs via
--custom-label-xml
- Re-run only statistics (and skip all registration and tensor estimation steps) with manually refined ROIs via
- Transform image volumes to-and-fro from diffusion and T1-coordinates via
--transform-diffusion-volumeand--transform-t1-volume. More options:- Only transform volumes (and skip all registration and tensor estimation steps) via
--only-transform-data - Specify interpolation method for transformation via
--transform-interpolation
- Only transform volumes (and skip all registration and tensor estimation steps) via
List of all BDP Flags
BDP Version: 21a (build #0081), released 2021-05-05
| Flags | Flag Description |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED FLAG | |
--nii <filename.nii.gz> |
Specifies the filename of the input diffusion data in 4D NIfTI-1 format. The flag must be followed by the filename. Only NIfTI-1 files with extension .nii or .nii.gz are supported. Furthermore, either the --bmat flag, or a combination of --bval (or -b) and --bvec (or -g) flags must be used to provide the necessary b-matrices or b-values and gradient vectors. |
| SCAN PARAMETERS FLAGS | |
--bval <filename> |
Specifies the filename of the file containing b-values for the diffusion scan. Either form of the flag can be used, followed by a filename. The b-value file must be a plain-text file and usually has an extension of “.bval“. This flag is only needed in conjunction with --nii. |
--bvec <filename> |
Specifies the filename of the file containing the diffusion gradient directions (specified in the voxel coordinates of the input diffusion-weighted image). Either form of the flag can be used, followed by the filename. The b-vectors file must be a plain text file and usually has an extension of “.bvec“. This flag is only needed in conjuction with --nii. |
--bmat <filename> |
Specifies the filename of the file containing b-matrices for diffusion-weighted scans. The flag must be followed by the filename. This file must be a plain text file containing 3×3 matrices for each diffusion encoding direction. It should contain zero matrices corresponding to b=0 images. This file usually has “.bmat” as its extension, and can be used to provide BDP with the more-accurate b-matrices as saved by some proprietary scanners. The b-matrices specified by the file must be in the voxel coordinates of the input diffusion weighted image (NIfTI file). This flag is useful only when used along with --nii. In case b-matrices are not known/calculated, .bvec and .bval files can be used instead (see --bvec and --bval). |
--dir=<direction> |
Specifies the phase-encoding direction of the EPI (diffusion) images. It is same as the dominant direction of distortion in the images. This information is used to constrain the distortion correction along the specified direction. Directions are represented by any one of x, x-, y, y-, z or z-. “x” direction increases towards the right side of the subject, while “x-” increases towards the left side of the subject. Similarly, “y” and “y-” are along the anterior-posterior direction of the subject, and “z” & “z-” are along the inferior-superior direction. When this flag is not used, BDP uses “y” as the default phase-encoding direction. |
--echo-spacing=<t> |
Sets the echo spacing to t seconds, which is used for fieldmap-based distortion correction. (Example: For an echo spacing of 0.36ms, use --echo-spacing=0.00036). This flag is required when using --fieldmap-correction. |
--bval-ratio-threshold <N> |
Sets a threshold which is used to determine b=0 images. When there are no diffusion weighted image with b-value of zero, then BDP tries to use diffusion weighted images with a low b-value in place of b=0 image. The diffusion images with minimum b-value is used as b=0 image only if the ratio of the maximum and minimum b-value is more than the specified threshold. A lower value of threshold will allow diffusion images with higher b-value to be used as b=0 image. The default value of this threshold is set to 45 when this flag is not used. The flag must be followed by a single number which specifies the threshold (Eg: --bval-ratio-threshold 65.5) |
| DIFFUSION MODELING FLAGS | |
--tensor |
Estimates diffusion tensors using a weighted log-linear estimation and saves derived diffusion tensor parameters (FA, MD, axial, radial, L2, L3). This is the default behavior if no diffusion modeling flags are specified. The estimated diffusion tensors can be visualized by loading the saved *.eig.nii.gz file in BrainSuite. BDP reports diffusivity (MD, axial, radial, L2 and L3) in a unit which is reciprocal inverse of the unit of input b-value. |
--FRACT |
Estimates ODFs using the Funk-Radon and Cosine Transformation (FRACT). The outputs are saved in a separate directory with name “FRACT” and the ODFs can be visualized by loading the saved “.odf” file in BrainSuite. |
--FRT |
Estimates ODFs using Funk-Radon Transformation (FRT). The coefficient maps for ODFs are saved in a separate directory with name “FRT” and the ODFs can be visualized by loading the saved “.odf” file in BrainSuite. The derived generalized-FA (GFA) maps are also saved in the output directory. |
--3dshore |
Estimates ODFs using the 3DSHORE basis representation. The outputs are saved in a separate directory with name “3DSHORE” and the ODFs can be visualized by loading the saved “.odf” file in BrainSuite. |
--gqi |
Estimates ODFs using the GQI method. The outputs are saved in a separate directory with name “GQI” and the ODFs can be visualized by loading the saved “.odf” file in BrainSuite. |
--erfo |
Estimates ODFs using the ERFO method. The outputs are saved in a separate directory with name “ERFO” and the ODFs can be visualized by loading the saved “.odf” file in BrainSuite. |
--diffusion_time_ms |
Sets the diffusion time parameter required for estimating ERFO, 3DSHORE, and GQI ODFs. This is a mandatory input when using the --erfo, --3dshore, or --gqi flag. |
--gqi-sigma |
Sets the GQI adjustable factor, required for calculating diffusion sampling length. The default value is set to 1.25. Paper suggests setting this parameter between 1 and 1.3. |
--3dshore-radord |
Sets the radial order of the 3D-SHORE basis, required for calculating 3D-SHORE ODFs. This is an optional parameter with the default value is set to 6. |
--snr |
Sets the SNR of the acquired data, required for calculating ERFO ODFs. This is an optional parameter with the default value is set to 35. |
--odf-lambda <L> |
Sets the regularization parameter, lambda, of the Laplace-Beltrami operator while estimating ODFs. The default value is set to 0.006. This can be used to set the appropriate regularization for the input diffusion data. |
| TRACKING FLAGS | |
--run_dsi_studio |
Sets the path of the DSI Studio installation. This is a mandatory flag to run tracking using BDP. This flag will call DSI Studio and estimate tracks for all the ODF methods that have been called. Please follow the flag with the DSI Studio installation path.This command saves the fib file and track file (.trk). |
--tracking_params |
Sets the tracking parameters for DSI Studio. This is an optional input. Please follow the flag with a string containing all the parameters in quotations. |
--save_fib |
Saves the fib file for all the ODF methods that have been called. A folder with name <ODF method>_FIB (e.g. ERFO_FIB) is created where the fib file is saved. |
--tracking_only |
BDP assumes that fib file was created in the previous run and skips all BDP steps. Then, it calls DSI Studio directly: bfc file, --nii, --bval, --bvec and --run_dsi_studio are mandatory inputs to be given with this flag. |
| CO-REGISTRATION FLAGS | |
--no-structural-registration |
Allows BDP to work without any structural input. This can useful when one is only interested in diffusion modelling part of BDP. With this flag only fieldmap-based distortion correction is supported. --output-fileprefix flag can be used to specify fileprefix of the output filenames. The flag --dwi-mask can be used to define region of interest for diffusion modelling. (see --output-fileprefix). |
--t1-mask <filename.nii.gz> |
Specifies the filename of the brain-mask file for input T1-weighted image. This mask can be same as the brain mask generated during BrainSuite extraction sequence. For best results, the mask should not include any extra-meningial tissues from T1-weighted image. The mask must be in the same coordinates as input T1-weighted image (i.e. should overlay correctly with input <fileprefix>.bfc.nii.gz file in BrainSuite). This mask is used for co-registration and defining brain boundary for statistics computation. The mask can be generated and/or edited in BrainSuite. In case --output-diffusion-coordinate is also used, this mask is first transformed to diffusion coordinate and the transformed mask is used for defining brain boundary in diffusion coordinates. When this flag is not used, BDP will try to use <fileprefix>.mask.nii.gz as brain-mask. If <fileprefix>.mask.nii.gz is not found, then BDP will use the input <fileprefix>.bfc.nii.gz itself as mask (i.e. all non-zero voxels in <fileprefix>.bfc.nii.gz is assumed to constitute brain mask). |
--dwi-masking-method <method> |
Specifies the method used for estimating a brain-mask for diffusion data, which is only used for registration purposes. Possible options are “hist” and “intensity“. “hist” the default method when this flag is not used which uses peaks and valleys in the histograms of intensity in the diffusion data to estimate a brain-mask. “intensity” method uses a heuristic approach based on the intensity of the b=0 image to estimate the brain-mask. The estimated (pseudo) brain-mask for diffusion data is saved as <fileprefix>.dwi.RSA.mask.nii.gz. In case co-registration is not accurate with this automatically generated (pseudo) mask, BDP should be re-run with a refined diffusion mask using the flag --dwi-mask. |
--dwi-mask <filename.nii.gz> |
Specifies the filename of the brain-mask file for diffusion data. This mask is used only for co-registration purposes and can affect overall quality of co-registration (see --t1-mask for definition of brain mask for statistics computation). The mask must be a 3D volume and should be in the same coordinates as input Diffusion file/data (i.e. should overlay correctly with input diffusion data in BrainSuite). For best results, the mask should include only brain voxels (CSF voxels around brain is also acceptable). The mask can be generated and/or edited in BrainSuite. When this flag is not used, BDP estimates a (pseudo) mask automatically: See flag --dwi-masking-method. |
--rigid-reg-measure <measure> |
Defines the similarity measure to be used for rigid registration. Possible measures are “MI“, “INVERSION” and “BDP“. MI measure uses normalized mutual information based cost function. INVERSION measure uses simpler cost function based on sum of squared difference by exploiting the approximate inverse-contrast relationship in T1- and T2-weighted images. BDP measure combines MI and INVERSION. It starts with INVERSION measure and refines the result with MI measure. BDP is the default measure when this flag is not used. |
--dcorr-reg-method <method> |
Defines the method for registration-based distortion correction. Possible methods are “MI“, “INVERSION-EPI“, “INVERSION-T1“, “INVERSION-BOTH“, and “BDP“. MI method uses normalized mutual information based cost-function while estimating the distortion field. INVERSION-based method uses simpler cost function based on sum of squared difference by exploiting the known approximate contrast relationship in T1- and T2-weighted images. T2-weighted EPI is inverted when INVERSION-EPI is used; T1-image is inverted when INVERSION-T1 is used; and both are inverted when INVERSION-BOTH is used. BDP method add the MI-based refinement after the correction using INVERSION-BOTH method. BDP is the default method when this flag is not used. |
--dcorr-regularization-wt <N> |
Sets the (scalar) weighting parameter for regularization penalty in registration-based distortion correction. This flag must be followed by a single non-negative number which specifies the weight (Eg: --dcorr-regularization-wt 0.5). A large regularization weight encourages smoother distortion field at the cost of low measure of image similarity after distortion correction. On the other hand, a smaller regularization weight can result into higher measure of image similarity but with unrealistic and unsmooth distortion field. A weight of 0.5 would reduce the penalty to half of the default regularization penalty (this weight is set to 1.0 when this flag is not used). Similarly, a weight of 2.0 would increase the penalty to twice of the default penalty. |
--no-distortion-correction |
Skips distortion correction completely and performs only a rigid registration of diffusion and T1-weighted image. This can be useful when the input diffusion images do not have any distortion or they have been corrected for distortion. |
--no-nonuniformity-correction |
Skips intensity non-uniformity correction in b=0 image for registration-based distortion correction. The intensity non-uniformity correction does not affect any diffusion modeling. |
--no-intensity-correction |
Disables intensity correction when performing distortion correction. Intensity correction can change the noise distribution in the corrected image, but it does not affect estimated diffusion parameters like FA, etc. |
| FIELDMAP FLAGS | |
--fieldmap-correction |
Use an acquired fieldmap for distortion correction. The fieldmap must have units of radians/second. The filename of the fieldmap file can be specified immediately after the flag. If the filename is NOT specified, BDP will look for a file with filename <fileprefix>.fieldmap.nii.gz in the same directory as the BFC file (<fileprefix>.bfc.nii.gz) and use it instead. Fileprefix must be same as the BFC fileprefix. The field of view (FOV) of the fieldmap scan must cover the FOV of the diffusion scan. BDP will try to check the overlap of the FOV of the two scans and will issue a warning/error if the diffusion scan’s FOV is not fully covered by the fieldmap’s FOV. BDP uses all of the information saved in the NIfTI header to compute the FOV. If you get this error and think that it is incorrect, then it can be suppressed using the flag --ignore-fieldmap-FOV. Neither the image matrix size nor the imaging grid resolution of the fieldmap needs to be the same as that of the diffusion scan, but the fieldmap must be pre-registred to the diffusion scan. BDP does NOT align the fieldmap to the diffusion scan, nor does it check the alignment of the fieldmap and diffusion scans. Only NIfTI files with extension of .nii or .nii.gz are supported. Fieldmap-based distortion correction also requires the --echo-spacing=<t> flag. Also see --fmap-least-square and --fmap-pixel-shift to define method for distortion correction. --fmap-least-square is the default method. |
--fieldmap-correction-method <method> |
Defines the distortion correction method while using fieldmap. Possible methods are “pixelshift” and “leastsq“. leastsq is the default method when this flag is not used. Pixel-shift (pixelshift) method uses image interpolation to un-distort the distorted diffusion images. Least squares (leastsq) method uses a physical model of distortion which is more accurate (and more computationally expensive) than pixel-shift method. leastsq cannot be combined with --no-intensity-correction. |
--ignore-fieldmap-fov |
Supresses the error generated by an insufficient field of view of the input fieldmap and continues with the processing. It is useful only when used with fieldmap-based distortion correction. See --fieldmap-correction for a detailed explanation. |
--fieldmap-smooth3=<S> |
Applies 3D Gaussian smoothing with a standard deviation of S millimeters (mm) to the input fieldmap before applying distortion correction. (Example: For Gaussian smoothing with a standard deviation of 2.5 mm, use --fieldmap-smooth3=2.5 ). This flag is only useful with --fieldmap-correction. Skip this flag for no smoothing. |
| TRANSFORMATION FLAGS | |
--transform-diffusion-volume <name> |
This flags allows to define custom volumes in diffusion coordinate which would be transformed into T1 coordinate in a rigid fashion. The flag must be followed by the name of either a NIfTI file or of a folder that contains one or more NIfTI files. All of the files must be in diffusion coordinate, i.e. the files should overlay correctly with the diffusion scan in BrainSuite. Only NIfTI files with an extension of .nii or .nii.gz are supported. The transformed files are written to the output directory with suffix ‘.T1_coord‘ in the filename and will not be corrected for distortion, if any. The flag --transform-interpolation can be used to define the type of interpolation that would be used (default is set to linear). If you are attempting to transform a label file or mask file, use “nearest” interpolation method with flag --transform-interpolation. See also --transform-t1-volume and --transform-interpolation. |
--transform-t1-volume <name> |
Same as --transform-diffusion-volume except that files specified must be in T1 coordinate, i.e. the files should overlay correctly with the input <fileprefix>.bfc.nii.gz files in BrainSuite. BDP transforms these data/images from T1 coordinate to diffusion coordinate. The transformed files are written to the output directory with suffix ‘.D_coord‘ in the filename. See also --transform-diffusion-volume and --transform-interpolation. |
--transform-interpolation <method> |
Defines the type of interpolation method which would be used while transforming volumes defined by --transform-t1-volume and --transform-diffusion-volume. Possible methods are “linear“, “nearest“, “cubic” and “spline” (all without quotes). When this flag is not used “linear” interpolation is used. |
--transform-t1-surface <name> |
Similar to --transform-t1-volume except that this flag allows transforming surfaces (instead of volumes) in T1 coordinate into diffusion coordinate in a rigid fashion. The flag must be followed by the name of either a .dfs file or of a folder that contains one or more .dfs files. All of the files must be in T1 coordinate, i.e. the files should overlay correctly with the T1-weighted scan in BrainSuite. The transformed files are written to the output directory with suffix ‘.D_coord‘ in the filename. |
--transform-diffusion-surface <name> |
Same as --transform-t1-volume except that the .dfs files specified must be in diffusion coordinate, i.e. the surface files should overlay correctly with the diffusion scan in BrainSuite. The transformed files are written to the output directory with suffix ‘.T1_coord‘ in the filename. See also --transform-t1-volume. |
--transform-data-only |
Skip all of the processing (co-registration, distortion correction and tensor/ODF estimation) and directly start transformation of defined custom volumes, mask and labels (using --transform-t1-volume, --transform-diffusion-volume, --transform-t1-surface, --transform-diffusion-surface, --custom-diffusion-label, --custom-t1-label). This flag is useful when BDP was previously run on a subject (or <fileprefix>) and some more data (volumes, mask or labels) need to be transformed across the T1-diffusion coordinate spaces. This assumes that all the necessary files were generated earlier and all of the other flags MUST be used in the same way as they were in the initial BDP run that processed the data. |
| STATISTICS FLAGS | |
--generate-stats |
Generate ROI-wise statistics of estimated diffusion tensor parameters. Units of the reported statistics are same as that of the estimated tensor parameters (see --tensor). Mean, variance, and voxel counts of white matter(WM), grey matter(GM), and both WM and GM combined are written for each estimated parameter in a separate comma-seperated value (.csv) file. BDP uses the ROI labels generated by Surface-Volume Registration (SVReg) in the BrainSuite extraction sequence. Specifically, it looks for labels saved in either <fileprefix>.svreg.corr.label.nii.gz or <fileprefix>.svreg.label.nii.gz. In case both files are present, only the first file is used. Also see --custom-diffusion-label and --custom-t1-label for specifying your own ROIs. It is also possible to forgo computing the SVReg ROI-wise statistics and only compute stats with custom labels if SVReg label is missing. BDP also transfers (and saves) the label/mask files to appropriate coordinates before computing statistics. Also see --output-diffusion-coordinate for outputs in diffusion coordinate and --force-partial-roi-stats for an important note about field of view of diffusion and T1-weighted scans. |
--generate-only-stats |
Skip all of the processing (co-registration, distortion correction and tensor/ODF estimation) and directly start computation of statistics. This flag is useful when BDP was previously run on a subject (or <fileprefix>) and statistics need to be (re-)computed later. This assumes that all the necessary files were generated earlier. All of the other flags MUST be used in the same way as they were in the initial BDP run that processed the data. |
--force-partial-roi-stats |
The field of view (FOV) of the diffusion and T1-weighted scans may differ significantly in some situations. This may result in partial acquisitions of some ROIs in the diffusion scan. By default, BDP does not compute statistics for partially acquired ROIs and shows warnings. This flag forces computation of statistics for all ROIs, including those which are partially acquired. When this flag is used, number of missing voxels are also reported for each ROI in statistics files. Number of missing voxels are reported in the same coordinate system as the statistics file. |
--custom-diffusion-label <name> |
BDP supports custom ROIs in addition to those generated by BrainSuite (SVReg) for ROI-wise statistics calculation. The flag must be followed by the name of either a file (custom ROI file) or of a folder that contains one or more ROI files. All of the files must be in diffusion coordinate, i.e. the label files should overlay correctly with the diffusion scan in BrainSuite. These input label files are also transferred (and saved) to T1 coordinate for statistics in T1 coordinate. BDP uses nearest-neighborhood interpolation for this transformation. Only NIfTI files, with an extension of .nii or .nii.gz are supported. In order to avoid confusion with other ROI IDs in the statistic files, a 5-digit ROI ID is generated for each custom label found and the mapping of ID to label file is saved in the file <fileprefix>.BDP_ROI_MAP.xml. Custom label files can also be generated by using the label painter tool in BrainSuite. See also --custom-label-xml. |
--custom-t1-label <name> |
Same as --custom-diffusion-label except that the label files specified must be in T1 coordinate, i.e. the label files should overlay correctly with the T1-weighted scan in BrainSuite. If flag --output-diffusion-coordinate is also used then these input label files are also transferred (and saved) to diffusion coordinate for statistics in diffusion coordinate. BDP uses nearest-neighborhood interpolation for this transformation. See also --custom-label-xml. |
--custom-label-xml <filename> |
BrainSuite saves a descriptions of the SVReg labels (ROI name, ID, color, and description) in an .xml file (brainsuite_labeldescription.xml). BDP uses the ROI ID’s from this xml file to report statistics. This flag allows for the use of a custom label description xml file. The flag must be followed by an xml filename. This can be useful when you want to limit the ROIs for which you compute statistics. You can also use custom xml files to name your own ROIs (assign ID’s) for custom labels. BrainSuite can save a label description in .xml format after using the label painter tool to create a ROI label. The xml file MUST be in the same format as BrainSuite’s label description file (see brainsuite_labeldescription.xml for an example). When this flag is used, NO 5-digit ROI ID is generated for custom label files and NO Statistics will be calculated for ROIs not identified in the custom xml file. See also --custom-diffusion-label and --custom-t1-label. |
| OUTPUT/CONFIGURATION FLAGS | |
--output-subdir <directory_name> |
By default, BDP writes out all the output (and intermediate) files in the same directory (or folder) as the BFC file. This flag allows to specify a sub-directory name in which output (and intermediate) files would be written. BDP will create the sub-directory in the same directory as BFC file. <directory_name> should be the name of the sub-directory without any path. This can be useful to organize all outputs generated by BDP in a separate sub-directory. |
--output-diffusion-coordinate |
Enables estimation of diffusion tensors and/or ODFs (and statistics if applicable) in the native diffusion coordinate in addition to the default T1-coordinate. All native diffusion coordinate files are saved in a seperate folder named “diffusion_coord_outputs“. In case statistics computation is required, it will also transform/save all label/mask files required to diffusion coordinate (see --generate-stats for details). |
--flag-conf-file <filename> |
Uses the defined file to specify BDP flags which can be useful for batch processing. A flag configuration file is a plain text file which can contain any number of BDP’s optional flags (and their parameters) separated by whitespace. Everything coming after # until end-of-line is treated as comment and is ignored. If a flag is defined in configuration file and is also specified in the command used to run BDP, then the later get preference and overrides the definition in configuration file. |
--output-fileprefix <fileprefix> |
Specifies output fileprefix when --no-structural-registration flag is used. The fileprefix can not start with a dash (-) and should be a simple string (Eg: --output-fileprefix Sub20-trial2 ). When this flag is not specified (and --no-structural-registration is used) then the output files have same file-base as the input diffusion file. This flag is ignored when --no-structural-registration is not used. |
--threads=<N> |
Sets the number of parallel process threads which can be used for computations to N, where N must be an integer. Default value of N is 4. |
--low-memory |
Activates low-memory mode. This will run the registration-based distortion correction at a lower resolution, which could result in a less-accurate correction. This should only be used when no other alternative is available. |
--ignore-memory |
Deactivates the inbuilt memory checks and forces BDP to run registration-based distortion correction at its default resolution even on machines with a low amount of memory. This may result in an out-of-memory error when BDP cannot allocate sufficient memory. |
| HELP FLAGS | |
--version |
Prints the version of the running BDP executable. All other flags and options are ignored and BDP terminates after printing out the version information. |
--check-for-updates |
Contacts the BrainSuite website to check for any available BDP updates and prints out a relevant message accordingly. All other flags and options are ignored and BDP terminates after checking for updates. |
--help |
Displays this message and then terminates. All other flags and options are ignored. |